Philadelphia Criminal Defense Blog
PA Superior Court Limits Deadly Weapon Used Sentencing Enhancement in Burglary Cases
The Deadly Weapon Used Enhancement does not apply unless the defendant used the deadly weapon while entering the building during a Burglary.
The Pennsylvania Superior Court has just decided the case of Commonwealth v. Tavarez. This decision limits the “Deadly Weapon Enhancement” for individuals convicted of burglary when a deadly weapon is involved. It requires that a sentencing court determine whether a deadly weapon was used in the commission of the burglary or whether a defendant merely possessed the deadly weapon at the time the defendant entered the building or occupied structure.
Commonwealth v. Tavarez
In Tavarez, the defendant pleaded guilty to one count each of aggravated assault, burglary, robbery, impersonating a public servant, and conspiracy. As part of his guilty plea, Mr. Tavarez stipulated to the following factual summary:
[O]n or about November 17th, 2015, shortly after 1:00 in the morning at 49 Mill Road in Oley Township, Berks County, Pennsylvania, you along with your accomplices and co-conspirators Edward Martinez, Brandon Smith, and Erick Green went to that residence; the plan even before - you arrived at the residence was to rob the people there; you believed that there were illegal drugs and money[] there to be gained; all four of you agreed to do that. When you got there, as was your intention all along, you and Edward Martinez entered the residence, there were people present. This was a residence. It was not open to the public at that time. You had no license or privilege to be there.
Once inside, you were yelling, [“]Police. Freeze[.”] in [an] attempt to compel the homeowners to do what you wanted them to do, thereby impersonating a public servant. Although you attempted to commit a robbery and you did so with firearms, nothing was actually taken.
When you confronted the homeowner, Eric Wegman, in the upstairs bedroom, he pulled his own handgun and fired, hitting both you and Mr. Martinez. Eric Wegman was also shot in the leg at that point.
Based on these facts, the trial court sentenced Mr. Tavarez to a 10 ½ to 30 years. The trial court did this, in part, by applying the “Deadly Weapon Used” enhancement to all of the charges, including the burglary charge. After he was sentenced, Mr. Tavarez filed a timely appeal. One of the issues Mr. Tavarez raised on appeal was whether the trial court erred in applying the “Deadly Weapon Used” enhancement to his burglary conviction.
What are the Sentencing Guidelines?
In Pennsylvania, an individual’s sentence will usually be determined by where the person falls on the sentencing matrix. The purpose of the sentencing matrix is to provide consistency in sentencing across the state. It is important to note that judges are not required to follow the guidelines and are free to depart from them when they see fit.
The first step in determining where a defendant falls on the sentencing matrix is to figure out what the individual’s Prior Record Score (“PRS”) is. A defendant’s PRS is based on their prior convictions. Specifically, a court will “add” up the prior record score points of each conviction. The more serious the offense, the more “points” it is worth. For example, if an individual’s sole conviction is for an Aggravated Assault where Serious Bodily Injury results, that person will have a PRS of 4. However, if an individual has two prior misdemeanor convictions, that are not specifically delineated by the General Assembly, then that individual will only have a PRS of 1.
The lowest PRS an individual can have is a 0. The highest PRS an individual can have is a 5. However, some individuals with multiple felony convictions can be classified as a REFEL, while some repeat violent offenders may be classified as a REVOC. These classifications will subject you to more severe guidelines. If you have previous convictions it is imperative that you have an attorney who understands how your PRS is calculated because it can have significant consequences on your sentence.
After the Prior Record Score is determined, the court must then determine the Offense Gravity Score (“OGS”) of the particular offense. The Pennsylvania General Assembly assigned an OGS for each offense listed in the Pennsylvania Crimes Code. The range of OGS is from 1-14, with 1 being the least serious, while 14 being the most serious.
In Tavarez, the defendant had a prior record score of 2. Additionally, the Burglary charge that Mr. Tavarez pleaded guilty to had an OGS of 9. Thus, if this was the only charge that Mr. Tavarez had pleaded guilty to his guidelines would have been 24-36 plus or minus 12. In Pennsylvania, a judge must sentence an individual to a minimum and maximum sentence. Assuming there were no additional enhancements (i.e. the “Deadly Weapon Enhancement”) and the court had sentenced him to a 2-4 year sentence that would have been a “guideline” sentence. However, because Mr. Tavarez agreed that he used a firearm, the court could, and did, apply the “Deadly Weapon Enhancement” to his case.
What is a Deadly Weapon Enhancement?
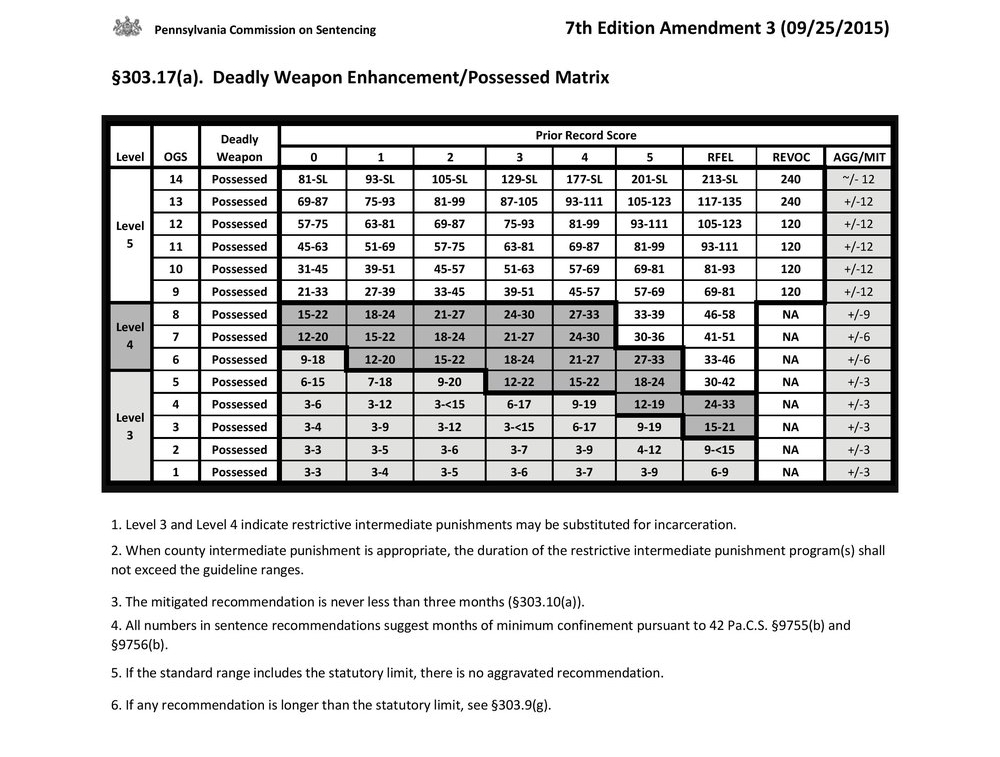
If someone commits a crime with a deadly weapon, a court must apply the “Deadly Weapon Enhancement.” This enhancement requires the court to look at additional matrixes to determine a sentence for the defendant. There are two types of deadly weapon enhancement charts: “Possession of a Deadly Weapon” and “Use of a Deadly Weapon.” The “Deadly Weapon Used” matrix will always recommend a more severe sentence than the “Deadly Weapon Possessed” matrix.
In Mr. Tavarez’s case, using his PRS of 2 and the OGS of 9 of the Burglary offense, the “Deadly Weapon Possessed” matrix had a guideline range of 33-45 plus or minus 12, while the “Deadly Weapon Used” matrix has a guideline range of 42-54 plus or minus 12. As such, there is a nine-month difference between the two guidelines which is very consequential.
The Superior Court holds that only the “Possessed” Matrix applies to Tavarez's Burglary Conviction.
Part of Tavarez's plea deal was to stipulate to a factual summary. After he filed his appeal, the Pennsylvania Superior Court reviewed the transcript and was limited to the facts that were on record. In Mr. Tavarez’s case, the record did not state that Mr. Tavarez used the firearm to commit the burglary. Further, in Pennsylvania, the crime of burglary ends once the felon breaks into the building because burglary is defined as breaking and entering a building or occupied structure with the intent to commit a crime therein. Therefore, the burglary is over once a defendant has entered a building even if the defendant goes on to commit other crimes once inside. Here, Tavarez admitted to using the firearm to rob the complainant after he had entered the residence. Consequently, the trial court was correct in applying the “Deadly Weapon Used” enhancement for the robbery and other offenses that he pleaded guilty to. However, because Mr. Talvarez had already completed the crime of burglary when he entered the complainant’s residence and did not use the firearm in the commission of the burglary, it was incorrect for the trial court to apply the “Deadly Weapon Used” enhancement for the burglary conviction. Because of this error by the trial court, the Superior Court remanded Mr. Talvarez’s case for resentencing.
Call the Award-Winning Criminal Defense Lawyers of Goldstein Mehta LLC if You Are Charged With a Criminal Offense
Philadelphia Criminal Defense Lawyers
As shown by Tavarez, the details in a case matter. If you are charged with any offense or under investigation by the authorities, you need a defense attorney who pays attention to the details that will make or break your case. Our award-winning Philadelphia criminal defense lawyers have successfully fought countless cases at trial and on appeal. We offer a 15-minute criminal defense strategy session to any potential client. Call 267-225-2545 to discuss your case with an experienced and understanding criminal defense attorney today.
Critical Mandatory Minimum Update
Critical Mandatory Minimum Update
Mandatory minimum sentencing laws in Pennsylvania may be about to change dramatically for the worse. For the past few years, the mandatory minimum sentences required by state law have been the subject of intense litigation, and most of them have been eliminated by opinions of the Pennsylvania Supreme and Superior Courts. Recently, the House passed a bill that would reinstate the previously stricken mandatory minimums by a vote of 146-46. The Philadelphia Inquirer reports that the Senate may also take up the legislation this week or next, and then the bill would be sent to the Governor for his signature.
Litigation Surrounding Mandatory Minimums
The litigation related to mandatory minimum sentences stems from the United States Supreme Court decision in Alleyne v. United States. In Alleyne, the Supreme Court held that because mandatory minimum sentences increase the penalty for a crime, any fact that increases the mandatory minimum is an “element” of the crime that must be submitted to the jury. For example, if the use of a firearm during the commission of a crime would trigger a mandatory minimum, as it previously did in Pennsylvania, then the fact that a gun was in fact used must be found by the jury at the end of trial instead of by the trial judge at sentencing.
Alleyne’s holding wreaked havoc on Pennsylvania’s mandatory minimum sentencing scheme. Instead of requiring that a jury rule on whether the facts which would trigger a mandatory minimum be submitted to the jury, Pennsylvania law specifically required the trial judge to determine if a mandatory minimum applied during sentencing. Further, the law permitted the sentencing judge to impose the mandatory minimum based on its own fact finding using a preponderance of the evidence standard instead of the much higher beyond a reasonable doubt standard required during a trial. For a defendant charged with selling drugs while in possession of a firearm, which previously triggered a five-year mandatory minimum, the sentencing judge could actually find that the mandatory minimum applied even if a jury had acquitted the defendant of possessing the gun but convicted the defendant of selling drugs.
The Pennsylvania sentencing scheme which gave this authority to the sentencing judge was in direct conflict with the Supreme Court’s holding in Alleyne. Therefore, in Commonwealth v. Hopkins, the Pennsylvania Supreme Court held that the Pennsylvania scheme was unconstitutional and struck down the vast majority of Pennsylvania mandatory minimum sentences.
Despite the rulings in Hopkins and Alleyne, a handful of significant Pennsylvania mandatory minimum sentences have survived. For example, mandatory minimums which are triggered based on the defendant’s prior record do not suffer from the same fatal flaw as the mandatory minimums surrounding the weight of drugs, the use of firearms, or other issues of that nature. Therefore, Pennsylvania’s three strikes law and DUI mandatory minimums continue to be enforced. In the case of the three strikes law, Pennsylvania imposes a mandatory minimum of 10-20 years of incarceration for certain second strikes and a sentence of 25 – 50 years for a third strike. The offenses which constitute strikes are listed in 42 Pa.C.S. § 9714 and include certain types of homicide, assault, robbery, burglary, and a number of sex offenses. Likewise, even a first offense DUI can trigger a 72-hour incarceration sentence when the defendant is not eligible for ARD. Because the sentencing judge must only be satisfied as to the fact that the defendant has a certain prior conviction, those mandatory minimum sentences have survived.
Although some mandatory minimums remain, most mandatory minimums were eliminated by Alleyne and Hopkins. For example, Pennsylvania previously had dozens of mandatory minimums for violent crimes committed with a firearm, based on the weight of drugs possessed with the intent to distribute, for selling drugs in a school zone, and for many sex offenses. This means that Pennsylvania had mandatory minimums not just for violent crimes, but also non-violent crimes like drug possession.
Problems with Mandatory Minimums
Mandatory minimums raise a number of serious problems. While most Americans probably believe that defendants properly convicted of serious violent felonies and sex crimes should receive prison time, mandatory minimums apply to all sorts of non-violent conduct such as the possession of narcotics. Further, mandatory minimums take a one-size-fits-all approach to sentencing which deprives the judge of the power to determine whether any given defendant is deserving of a break due to something in the defendant’s background. For example, even if the judge learns at sentencing that the defendant in a drug case is dying of cancer, the judge would be unable to impose anything less than the mandatory minimum of incarceration in a state prison.
Finally (and perhaps most importantly), mandatory minimums force innocent people to plead guilty in order to avoid the risk of facing the mandatory minimum. When a defendant is charged with a crime that would trigger 25-50 years in prison should the defendant lose at trial, the defendant is much more likely to take a deal if the prosecutor offers probation. This is true regardless of whether or not the defendant actually committed the crime. Thus, many people who are actually innocent plead guilty in order to avoid the mandatory minimum instead of taking the case to trial. This is a huge contributing factor to the fact that the overwhelming majority of criminal cases end in some form of plea deal. Mandatory minimums have likewise led to a huge increase in the prison population in Pennsylvania and the rest of the country.
What to Do
If you are a Pennsylvania citizen, it is not too late to contact your State Senator and Governor Wolf and ask them to oppose the enactment of mandatory minimum sentences. Defendants should not have to plead guilty to crimes that they did not commit because they cannot risk the imposition of a mandatory minimum sentence. Additionally, each defendant is different, and many defendants charged with mandatory minimum crimes simply are not deserving of incarceration. Mandatory minimums take the authority to figure out who may be rehabilitated with probation or house arrest away from a neutral judge and give that power to the prosecutor who may be more interested in obtaining convictions and lengthy sentences for political reasons.
Contact a Philadelphia Criminal Defense Lawyer Today
If you are currently charged with or could be charged with a crime, then you should contact an experienced criminal defense attorney immediately. When you are deciding how to attack the case, one of the first things you need to know is whether a mandatory minimum could apply to some of the charges you are facing. The Philadelphia Criminal Defense Lawyers of Goldstein Mehta LLC have extensive experience fighting all types of state and federal charges in Pennsylvania and New Jersey, and we will be able to evaluate your case, determine if a mandatory minimum applies, and provide you with the best options and advice on how to proceed. Call 267-225-2545 now for a free consultation.